Target Directory Configuration
About Target Directory
Target Directory is the user/group directory used for authentication when a user runs a search query.
- For example, if the search user interface expects an Active Directory user when logging in, then Active Directory must be configured.
- Related settings can be found on a separated tab on the Configuration Settings page.
- Currently three types of target directories are supported:
- Active Directory
- Azure Active Directory
- Microsoft Search Target Directory (to be used when indexing with Microsoft Search Target)
Configuring Active Directory
When you select Active Directory from the drop-down list, the related settings are displayed:
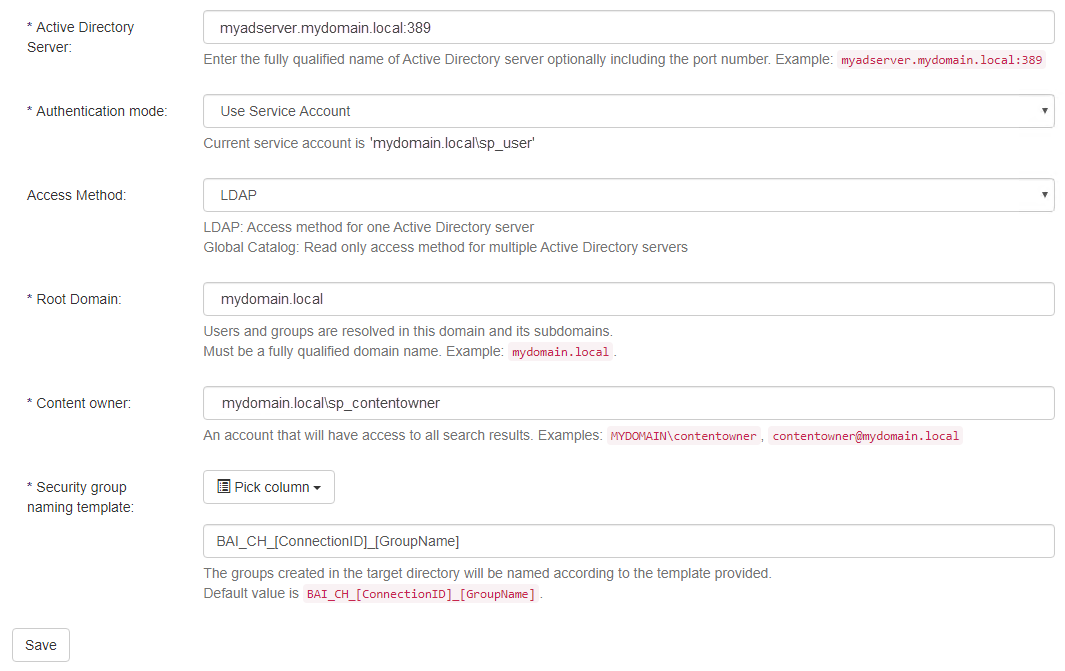
Active Directory Server
Host name or IP address of the Active Directory server.
Port number is optional and must be specified only if different from the default (389) port.
Authentication Mode
Two different authentication modes are supported:
- User Service Account
- The application pool / service account will be used to authenticate, what was specified during Connectivity Hub installation.
- This mode is supported only if that account is a domain account.
- Specify User Account
- Any user name and password can be specified here to authenticate.
Access Method
- By default, Connectivity Hub uses the LDAP protocol to communicate with Active Directory.
- If multiple domain controllers are used, then a specific one can be a "global catalog server" containing cached information from all other controllers.
- If configured, the server must be used as a global catalog, and that option must be selected here.
Root Domain
When Connectivity Hub gets a user or group from Active Directory it does so under this domain only.
For example, if root domain is set to "department1.mydomain.com", then users and groups under "department2.mydomain.com" will be unknown to Connectivity Hub.
Content Owner
The user configured here has permission to see any items in the search index.
- You must use the fully qualified domain name here
- For example, "MYDOMAIN\Administrator" is not allowed
- Correct format: "mydomain.com\Administrator"
Security Group Naming Template
The groups created in the target directory are named according to the template provided. The default value is displayed in the user interface.
Configuring Azure Active Directory
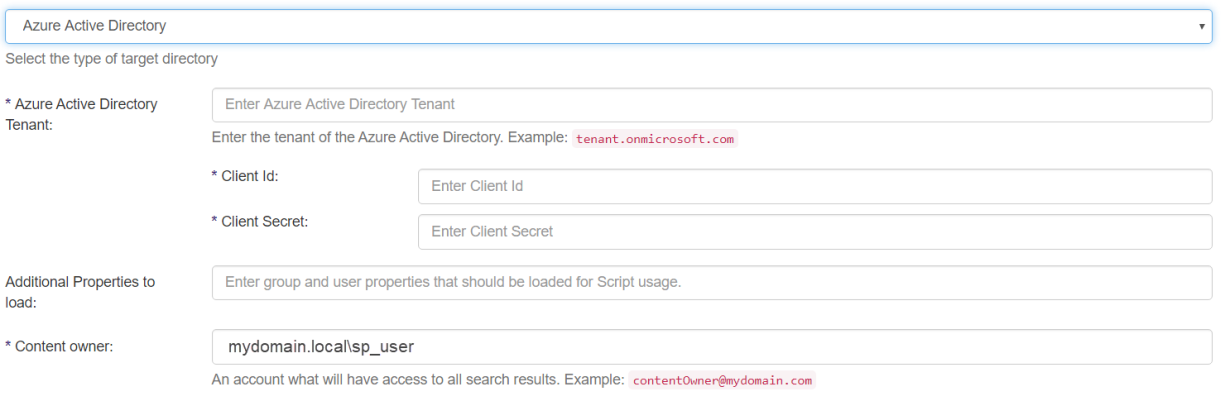
If Azure Active Directory is selected from the drop-down list, then related settings are displayed:
Azure Application Configuration
An Azure application must be configured and granted the following permissions for the Graph API:
- Member.Read.Hidden
Read all hidden memberships - GroupMember.Read.All
Read group members - Directory.Read.All
Read users and groups - User.Read.All
Read all users' full profiles
Azure Active Directory Tenant
The tenant name must be added in the following format: tenantName.onmicrosoft.com
Client ID
- The ID of the application registered on the tenant.
- Used to get Azure Active Directory user and group data.
Client Secret
- The Client Secret of the application registered on the tenant.
- Used to get AAD user and group data.
Default Properties
By default the following properties are loaded for users and groups:
- Id
- DisplayName
- OnPremisesSecurityIdentifier
- AccountEnabled
- DeletedDateTime
- UserPrincipalName
Additional Properties to Load
A list of additional properties loaded for users and groups when performing a security sync or a crawl.
Content Owner
The user configured here has permission to see any items in the search index.
The user account must be entered in the following format: contentOwner@myDomain.onmicrosoft.com
Configuring Microsoft Search Directory
When to use this directory:
-
Configure this target directory if you are indexing your content with the Microsoft Target.
-
This directory enables the creation and synchronization of the connector groups.
Restrictions
-
If you are using SmartHub as a search center, the Microsoft Search directory is unavailable.
-
Use the Azure target directory instead.
Because the same Microsoft connection will be used to store your groups and your content, make sure to completely prepare your content for indexing before running the Security Sync task.
To index secured content with Microsoft Search use the following steps:
- Create your Connection
- Under the tab Security:Directory, check Create security groups: If checked, missing security groups will be created in the target directory during Security Sync.
- Create you content and map it to your Microsoft Search target
- Run the datastore types task
- Run the datastore load task
- Review metadata settings and make sure your schema is compliant with the Microsoft search restrictions
- Run the security sync task
- Run the content synchronization task
Azure Application Configuration
An Azure application must be configured and granted the following permissions for the Graph API:
- Group.ReadWrite.All
- User.Read.All
- ExternalItem.ReadWrite.All
Note: To configure the Microsoft Search directory follow the above instructions for Azure Target directory setup.