Automatic Percent Complete Methods
If you are using a calculated percent complete, PowerSteering uses one of three methods to determine the percent complete: Task-based, Duration-based, or Effort-based.
- Pros: A calculated percent complete method provides a concrete explanation for how the percent complete is calculated without depending on someone's instinct.
- Cons: Users may miss the flexibility of using the manual approach to set the percent complete value.
Note: Unless defined at the template level, the default for all new projects will be Manual. See Change the Way PowerSteering Calculates the Percent Complete for a Project for more information about changing the percent complete method.
1. View Percent Complete Method
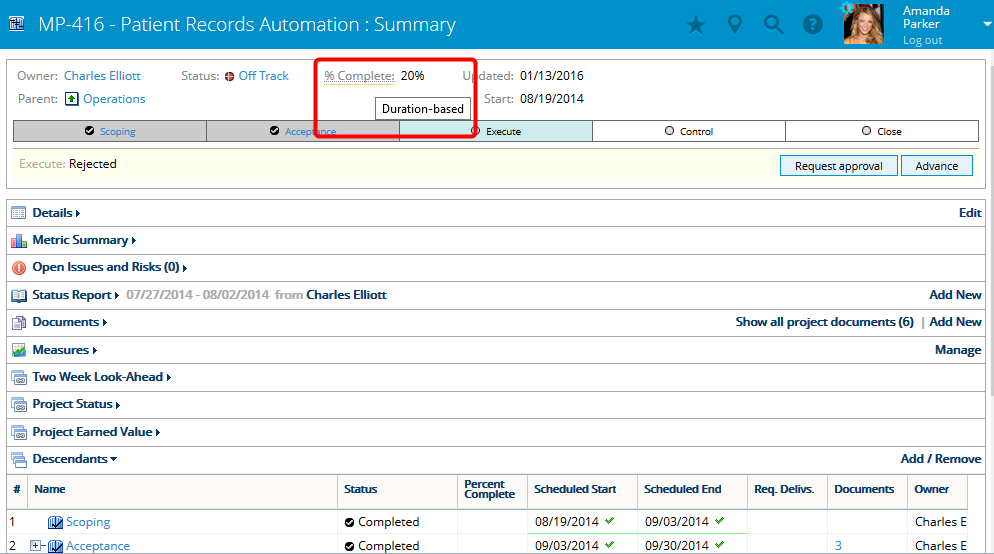
- For calculated percent complete methods, you are able to hover over % Complete on the Summary page to view which method is being used.
Note: PowerSteering will not display any percentages at milestones or gates.
2. Task-based
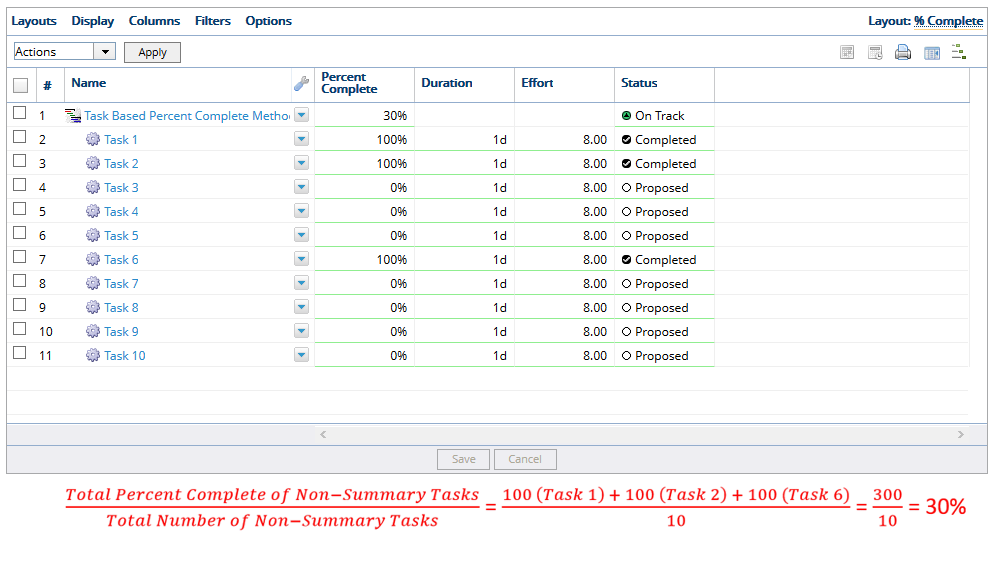
- The task-based percent complete method calculates the percent complete by counting the total percent complete of non-summary tasks in the project schedule, divided by the total number of non-summary tasks for the project. If milestones and document deliverables are included in your project plan, they will be part of the task-based percent complete calculation. In the example above, there are 10 summary tasks and 3 of them are 100% complete, so PowerSteering updates the Percent Complete to 30%.
2.1 Partially Completed Tasks
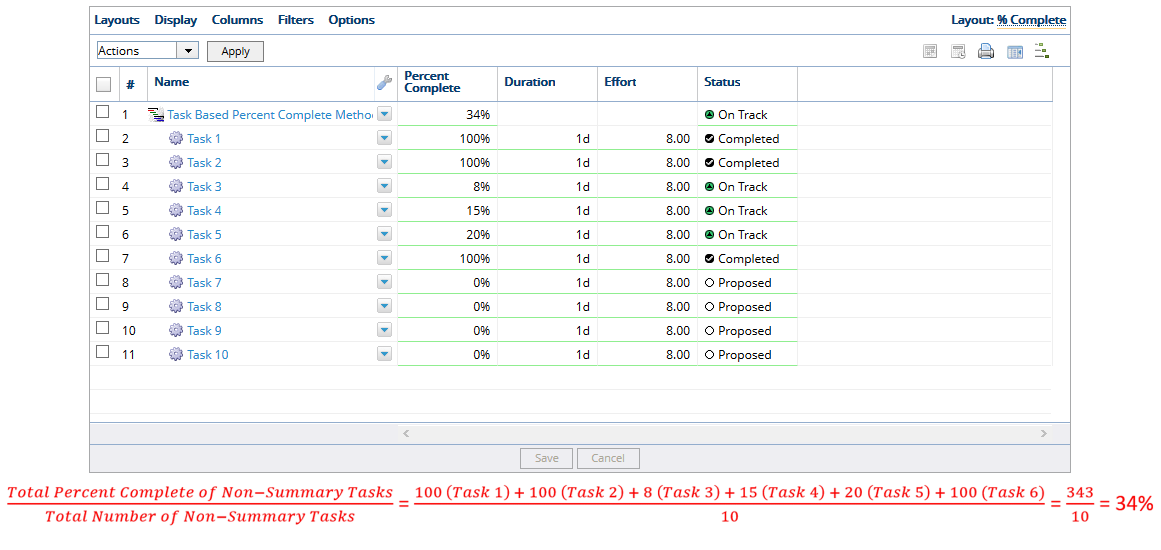
- In the example above, there are 10 summary tasks, 3 of them are 100% complete and others are partially complete, so PowerSteering updates the Percent Complete to 34%.
2.2 Canceled Tasks
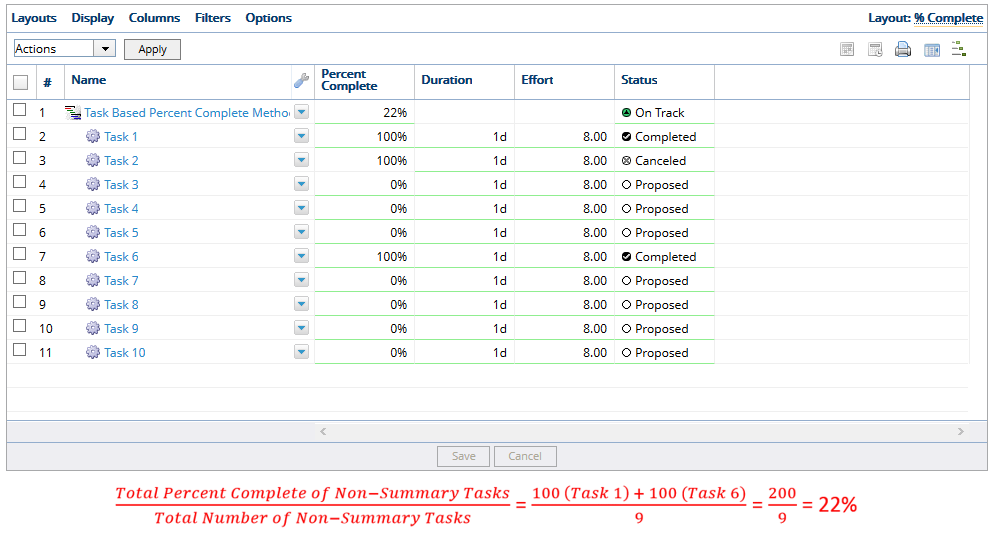
- When a task is canceled, the value is removed from the percent complete calculation and the percent complete value of the task and its actual dates cannot be edited. In the example above, Task 2 was canceled; therefore, it is removed from the project leaving 9 summary tasks, so PowerSteering updates the Percent Complete to 22%.
2.3 Summary Tasks
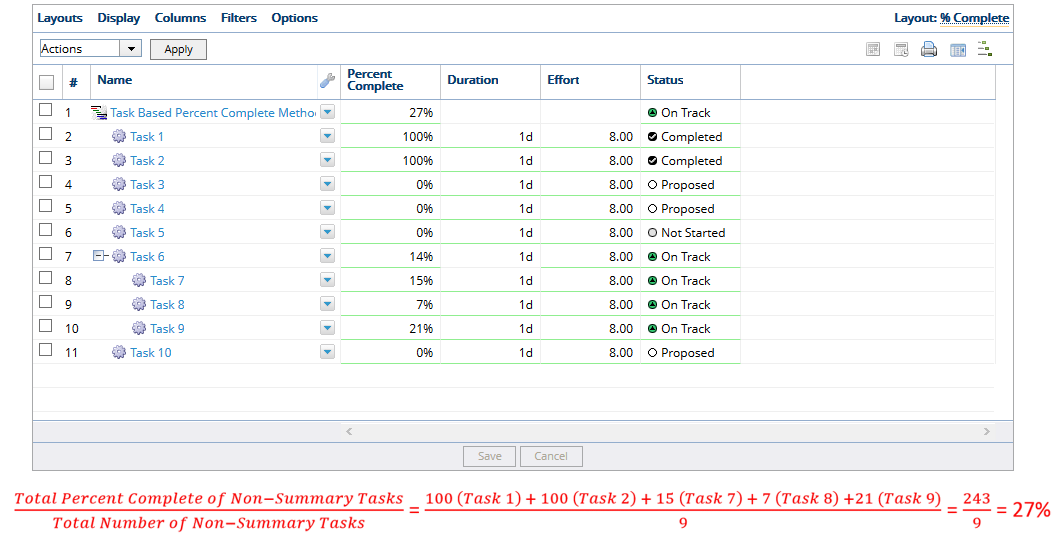
- Summary tasks are not included in the percent complete calculations. In the example above, Task 6 is a summary task; therefore, it is removed from the calculation leaving 9 summary tasks, so PowerSteering updates the Percent Complete to 27%.
3. Duration-based
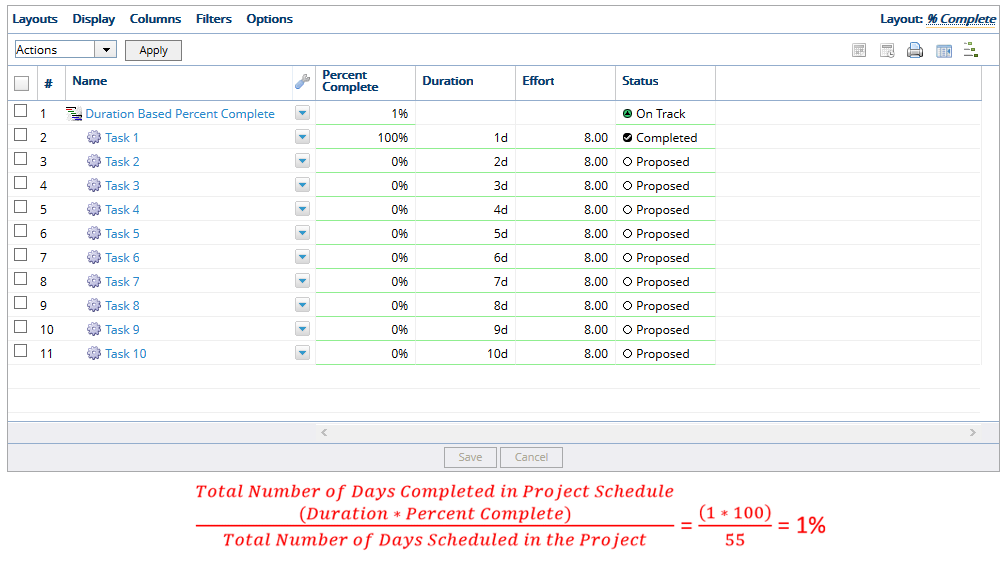
- The duration-based percent complete method calculates the percent complete by counting the total number of days completed in the project schedule, divided by the total number of days scheduled for the project. The total number of days completed for a work item is its duration multiplied by its percent complete. In the example above, there are 55 days total in the project plan, and the duration for Task 1 is 1 day, so PowerSteering updates the Percent Complete to 1%.
3.1 Partially Completed Tasks
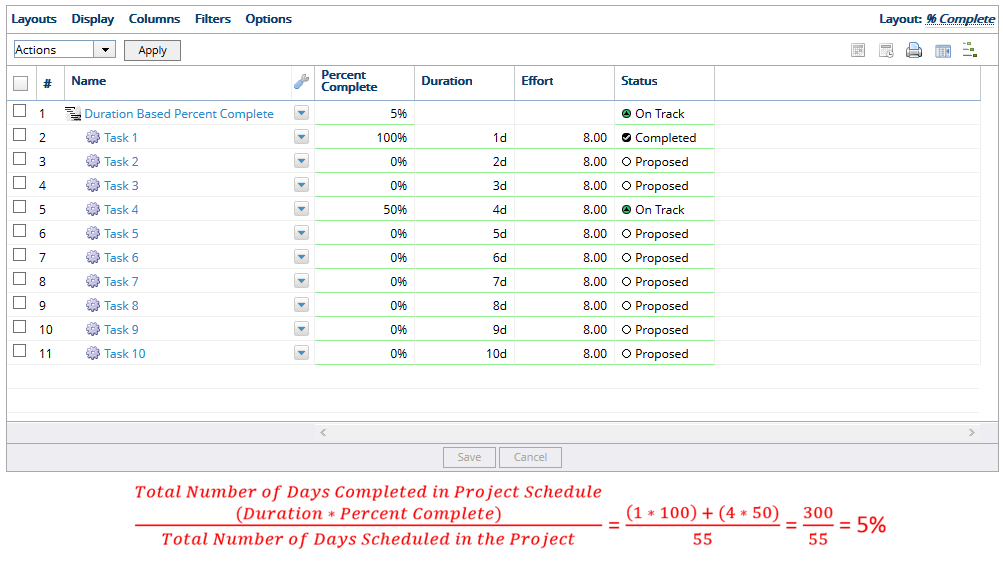
- In the example above, Task 1 has a duration of 1 day and is 100% complete and Task 4 has a duration of 4 days and is 50% complete, PowerSteering updates the Percent Complete to 5%.
4. Effort Based
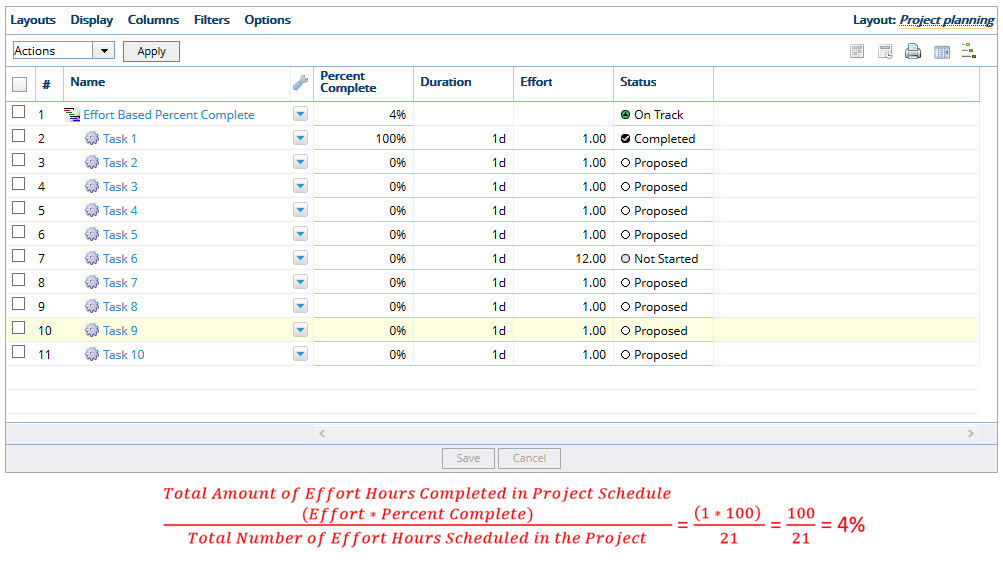
- The effort-based percent complete method calculates the percent complete by the total amount of effort hours completed in the project schedule divided by the total number of effort hours planned in the project. The total amount of hours completed for a work item is its effort percent complete multiplied by its effort. In the example above, there are 21 effort hours total in the project plan, and the effort for Task 1 is 1 hour, so using the calculation, PowerSteering updates the Percent Complete to 4%.
4.1 Partially Completed Tasks
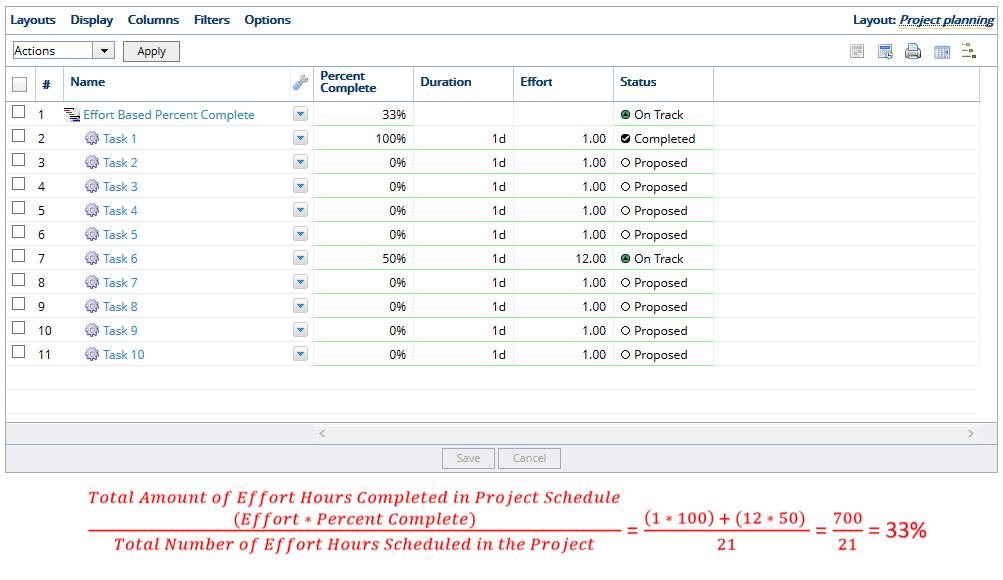
- In the example above, Task 1 has effort of 1.00 and is 100% complete and Task 6 has effort of 12.00 and is 50% complete, so PowerSteering updates the Percent Complete to 6%.