How to Integrate Metrics Into Your Search
- Integrating metrics into your search gives you the power to find data based on aggregations of information stored in Elastic.
- This functionality works on top of Elastic's aggregation capability and in combination with the collapsing functionality.
- The Elastic Aggregator stage is a native, built-in stage that works on top of the Elastic backend The search engine your SmartHub instance uses to perform queries. SmartHub can be configured to use more than one search engine..
- The stage has to be added both as a Query and Results stage.
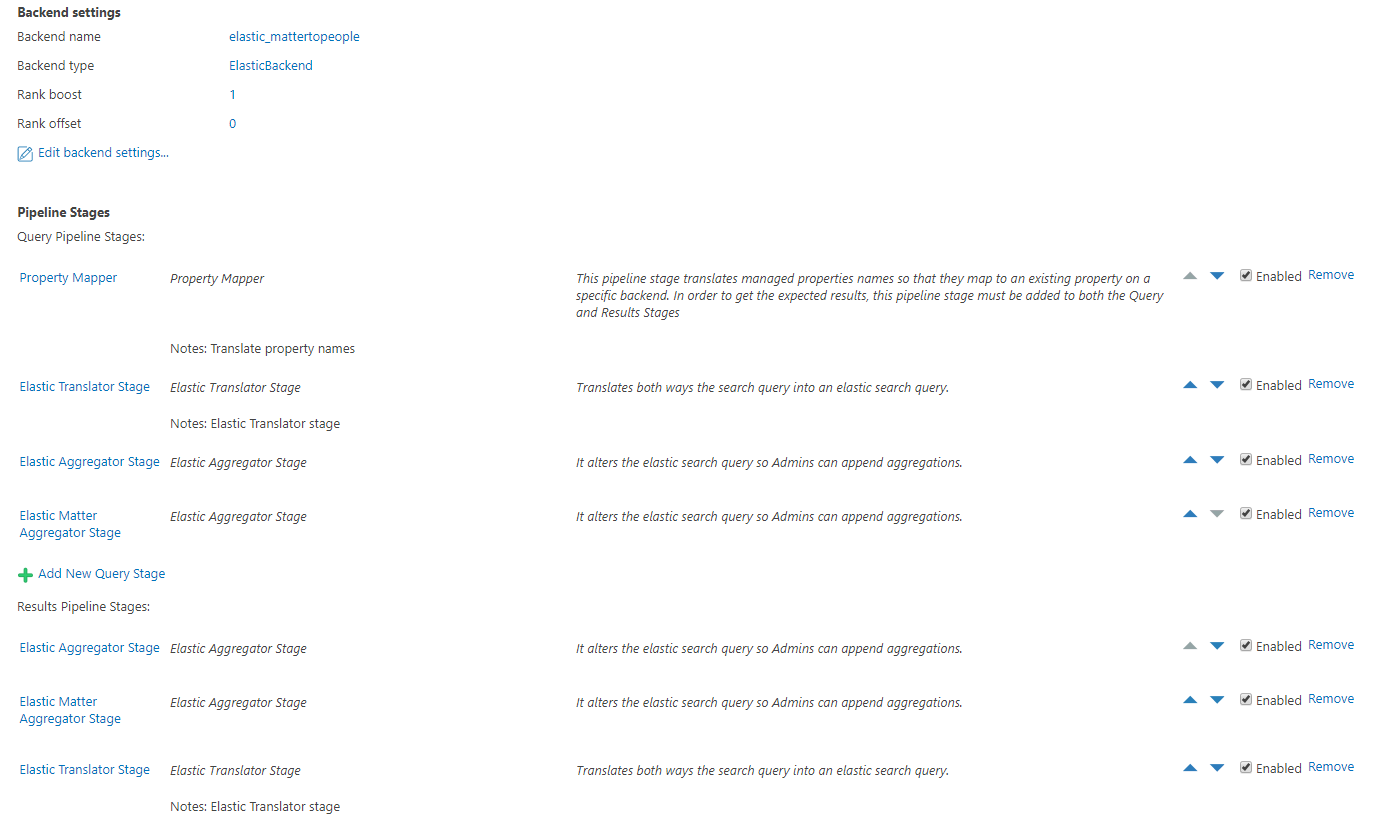
Pipeline Stages
- A Results stage has to be added first on the list with pipeline stages, because it is an Elastic translator stage.
- A Query stage has to be added last on the list with pipeline stages, after the Elastic translator stage.
Stage Parameters
- For every search interface (every content by search and main search results) add a new set of Elastic Aggregator stages.
- Separate the execution flow by specifying a different Result source ID.
|
Related record property |
<no default> |
The name of the elastic property that is used to calculate how to attach aggregated values to the search results. Example: _PEOPLENAME _MATTERID |
|
Maximum number of records |
500 |
Maximum number of records returned – this is needed, so we can re-sort the results based on the aggregation via post-processing. |
|
Result source ID |
<no default> |
Enables you to restrict the stage to execute only on some queries based on the matching result source ID. |
|
Aggregation JSON |
<no default> |
Example: Example
{
"aggs": {
"hoursByPeople": {
"terms": {
"field": "_PEOPLENAME",
"size": 2147483647
},
"aggs": {
"workedhours": {
"sum": {
"field": "_WORKEDHOURS" }
}
}
}
}
}
{
"aggs": {
"hoursByMatter": {
"terms": {
"field": "_MATTERID",
"size": 2147483647
},
"aggs": {
"matterworkedhours": {
"sum": {
"field": "_WORKEDHOURS" }
}
}
}
}
}
|