Query Jobs
This is the last section of the external database tutorial, after completing Store job information.
To complete the commingling sample, the process of combining multiple documents into a single output, you’ll create a flow that retrieves and merges all jobs created today.
Overview
The flow is triggered manually using an inject node, which executes a query to retrieve all jobs created on the current day. Alternatively, the inject node can be configured to run on a schedule, for example, once a day at a specific time, to automatically trigger the commingling process without manual intervention.
The database query returns an array of contentSetId values, which is passed to a paginated output node to generate the combined output stream, in this example, a single PDF file.
After the output is generated, the flow updates each job record in the database with a batchId, which is a file system–friendly timestamp string. This same string is also used as the folder name in the output directory, keeping the generated files organized and easy to trace back to their corresponding job batch.
Retrieving today’s jobs
The first part of the commingling flow retrieves all jobs created on the current day.
This section uses an inject node, a function node to prepare the SQL query, and a mysql node to execute it, similar to what you configured in the earlier sections of this tutorial.
Add the nodes
-
Add an inject node to the canvas.
-
This is used to trigger the flow manually, like the sample data injection.
-
The flow can also be configured to run on a schedule, but for this example it is manual.
-
-
Add a function node after the inject node.
-
This node prepares the SQL query that retrieves jobs created today from the database.
-
Use the JavaScript below to set up the query and parameters.
-
msg.topic = `
SELECT contentset_id
FROM olca_daysets.jobs
WHERE DATE(creation_date) = CURDATE()
AND status = 'queued'
`
return msg-
Add a mysql node after the function node.
-
Configure it to connect to the MariaDB host and database (schema) created earlier in Set up Database.
-
The MySQL node executes the SQL statement provided in
msg.topicusing the parameters defined inmsg.payload.
-
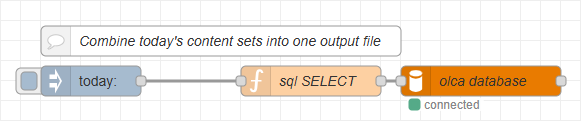
How the query works
The SELECT statement returns all records created today using WHERE DATE(creation_date) = CURDATE(). This condition extracts the date portion of the creation_date column (ignoring the time) and filters the results to include only the jobs created today.
The result in msg.payload looks like this:
[
{
"contentset_id": 5278441
},
{
"contentset_id": 5278442
},
{
"contentset_id": 5278443
}
]
Creating output
Before generating the combined document, we need to transform the query result into the data expected by the paginated output node and prepare a batch identifier for the output folder.
Adding the nodes
-
Add a switch node after the mysql node to continue only when the database returns IDs.
-
In Properties, set the Property field to
msg.payload. -
Select the condition to
is not empty.
-
-
Add a change node and create three rules:
-
Set
msg.contentSetIdto the following J: expression:Copy$map(payload, function($v){ $v.contentset_id} ) -
$maplets you loop through an array and apply a function or expression to each item, returning a new array with the results. In this case, you are extractingcontentset_idto create a clean array, which is used by the paginated output node: The result looks like this:[5278441,5278442,5278443] -
Set
msg.batchIdto the following J: expression:Copy$moment().format("YYYYMMDD_HHmmss") -
This creates a file-system–friendly timestamp. It is both as the
batch_idin the database (if needed) and builds a dynamic output folder. -
Set
msg.outputFolderto the following J: expression:Copy"C:/workspace/daysets/out/" & batchId
-
-
Add a paginated output node after the change node:
-
Set the Output Method to:
Send File(s) to Folder -
Set the Folder option to
msg.outputFolder -
Enable the Create directory if it does not exist option
-
-
This produces the final combined output (e.g., PDF) in a per-batch folder named with your timestamped batchId.
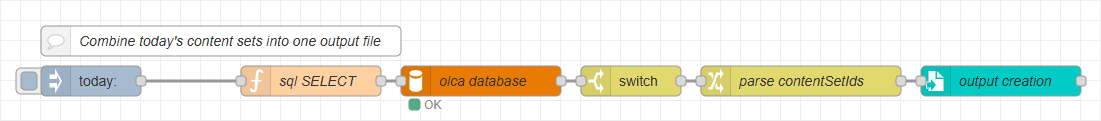
Marking Records as Complete
After generating the combined output, you’ll update the related job records with the batchId and mark them completed. In this sample, you store the batchId directly on each job. In production, you may prefer a separate batches table and a foreign key from jobs → batches to track extra statistics like document count, sheet count, etc.
Finally, you’ll mark the processed content sets for deletion since they’re no longer needed.
Adding the Nodes
-
Add a function node after the paginated content node.
-
This prepares an update for all content sets in
msg.contentSetId:-
sets
status = 'completed' -
sets
batch_id = msg.batchId -
sets
completed_date = NOW()
-
-
Use the JavaScript below to set the updates. Enter this for the On Message tab.
-
// Preparing the SQL statement using named parameters
msg.payload={}
msg.payload.contentSetId = msg.contentSetId
msg.payload.batchId = msg.batchId
msg.payload.jobStatus = "completed"
msg.topic = `
UPDATE olca_daysets.jobs SET status = :jobStatus, batch_id = :batchId, completed_date = NOW() WHERE contentset_id IN (:contentSetId)
`
return msg-
Add a mysql node after the function node
This executes the update in
msg.topicwith parameters frommsg.params. -
Add mark sets for deletion node.
-
This flags the generated content sets for cleanup in OL Connect’s File Store.
-
Set Entity to
Content Set. This adds the Content Set field to Properties. -
Set Content Set to
msg.contentSetId(the array used for this batch)
-
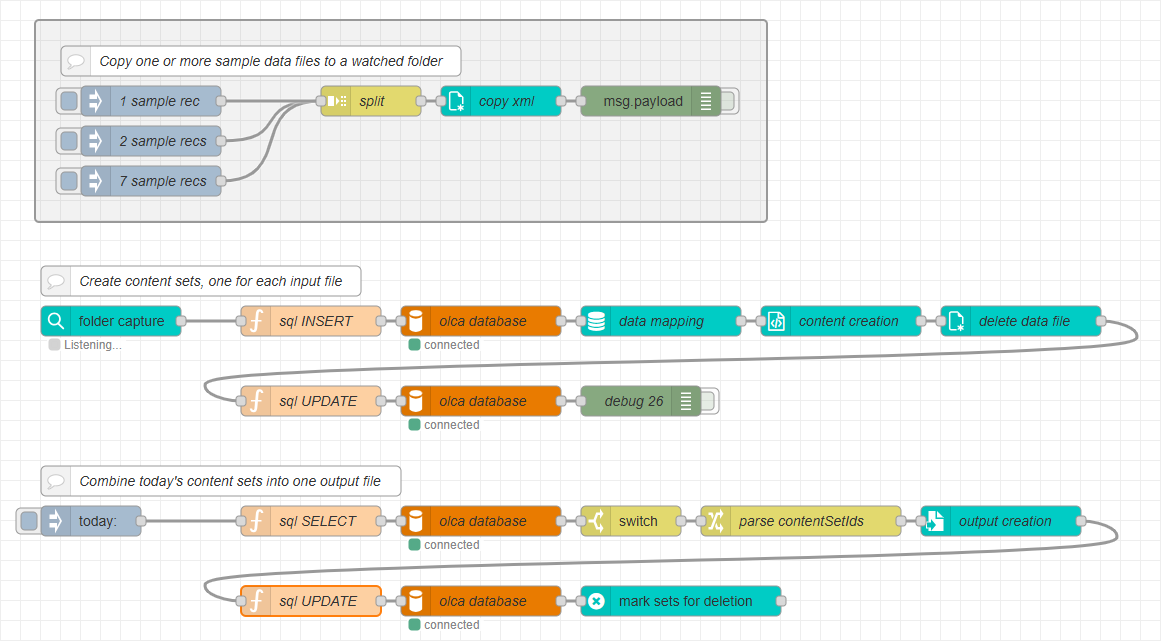
This completes the basic commingling flow using an external database:
-
Jobs are inserted/updated as they arrive.
-
Paginated content is generated and combined.
-
A
batchIdgroups the day’s output and is written back to the jobs. -
Content sets are marked for deletion.
Dashboards and triggers are out of scope for this tutorial, but will be covered in a future tutorial.