Store job information
This continues the external database tutorial, after completing Set up Database.
In this section you’ll set up a simple flow to store job information in the database. To make testing easier, you start with a sample data injection flow, a technique described in the Automate sample data testing. This allows you to test with various data files directly from flow editor, without manually copying files into the hot folder.
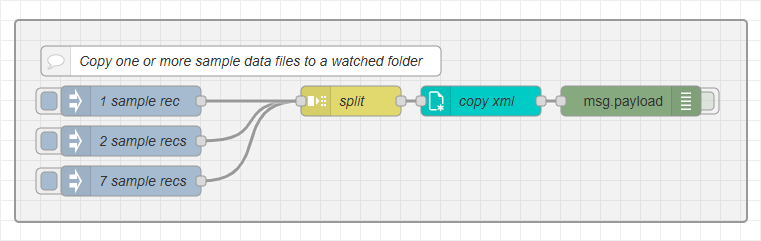
Sample data testing flow
Here’s how it works:
-
The flow contains several inject nodes, each configured to simulate a different test case.
-
When triggered, an inject node inserts an array of sample file names into
msg.payload. -
A split node receives this array and iterates over each file name, ensuring that the flow processes one entry from the array at a time.
-
A file operations node uses an JSONata expression to dynamically compose the source and target paths for each file based on its name.
-
The source path points to the file within the project’s
datafolder. -
The target path points to the designated hot folder configured using the folder capture node.
-
This technique allows you to quickly trigger file-based workflows using realistic test data, an efficient way to validate your database storage and job tracking logic, without needing to manually manage files in the operating system. The name of each file is unique mimicking data files written by an external system.
Write the job record flow
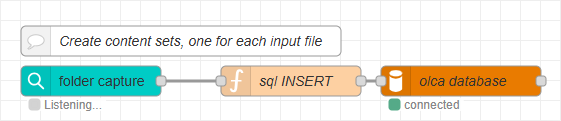
With the database configured and the sample data flow in place, you can build the flow that stores job information and creates content items. In this section, you insert the job file name into the jobs table whenever a new file appears in the hot folder. The goal is to capture the file event and add a corresponding record to the database using the received file name.
Add the nodes
-
Add an folder capture node.
-
Configure it to monitor your hot folder for new files. Sample path:
C:\workspace\daysets\in -
When a new file appears, the node outputs file metadata in msg.file.
-
-
Add a function node after the folder capture node.
-
This node prepares the SQL query that inserts a new job record into the database.
-
Use the JavaScript below to set up the query and parameters.
-
// Preparing the SQL statement using named parameters
// msg.payload can contain an array of values to bind to the topic.
// msg.topic must hold the query for the database.
msg.payload={}
msg.payload.fileName = msg.file.name
msg.payload.jobType = 'letter'
msg.topic = `
INSERT INTO olca_daysets.jobs(file_name, job_type) VALUES (:fileName,:jobType)
ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE creation_date = NOW(), status = 'initialized', completed_date = NULL, batch_id = NULL
`
return msg-
Add a mysql node after the function node.
-
Configure it to connect to the MariaDB host and database (schema) created earlier in Set up Database.
-
The MySQL node executes the SQL statement provided in
msg.topicusing the parameters defined inmsg.payload.
-
How the Query works
-
The query inserts the received file name into the database and sets the
job_type:type to letter. -
The
ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATEclause ensures that if a record already exists with the same unique key (in this case,file_name), the existing record is updated instead of a new one created. -
When a job is re-invoked for the same data file, for example, after modifying text or updating content, the statement updates the
creation_date, resets thecompleted_date, and resets the job’sstatusto initialized.
This approach ensures that the database always reflects the most recent state of each job file while maintaining a single consistent record per file.
To prevent SQL injection attacks, always escape or sanitize any user-provided data before including it in an SQL query. It’s a best practice to use an escaping or formatting helper (such as sqlstring) whenever you need to interpolate values directly into SQL statements. This library can be loaded as a module within a function node (Setup tab), however, this is not covered in this tutorial.
Add the OL Connect nodes
The next part of the flow handles data processing and content generation using OL Connect nodes. These nodes transform the incoming job data into paginated content and then clean the input files
Add the nodes
-
Add a data mapping node after the mysql node.
-
Set its Server field to the server configuration of your OL Connect instance.
-
Select the data mapping configuration that was created to process the incoming data files.
-
-
Add a paginated content node after the data mapping node.
-
Set its Server field to your OL Connect instance.
-
Select the template for these jobs.
-
This node merges the mapped data with the selected OL Connect template, creating a paginated content set. When successful, the node outputs a reference to the generated content in
msg.contentSetId.
-
-
Add a file operations node paginated content node.
-
Set its Operation to
Delete. -
Enter the
path.filename. -
This node deletes the original input data file once it has been processed successfully.
-
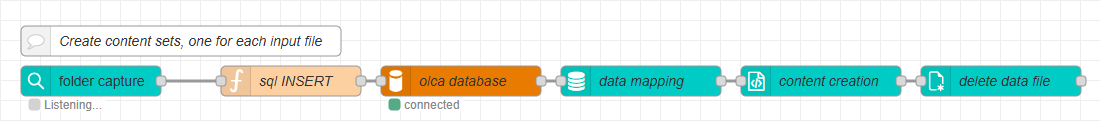
At this stage, the flow has created the merged and paginated content in OL Connect’s file store, and the paginated content node has returned the generated content reference in msg.contentSetId.
In the next section, you’ll learn how to update the corresponding database record for this job with this contentSetId, which allows the system to combine all generated content sets at the end of the day.
Update the record
In this final step, you’ll update the database record for the data file currently being processed. The update includes the contentSetId returned by the paginated content node and sets the status to queued.
The nodes required for this step are the same as those used in the initial database insert: a function node to prepare the query and a mysql node to execute it.
Add the Nodes
-
Add a function node after the file operations node.
-
This node prepares the SQL query that updates the existing job record in the database.
-
Use the JavaScript below to set up the query and parameters.
-
// Preparing the SQL statement using named parameters
msg.payload={}
msg.payload.fileName = msg.file.name
msg.payload.contentSetId = msg.contentSetId
msg.payload.jobStatus = "queued"
msg.topic = `
UPDATE olca_daysets.jobs SET contentset_id = :contentSetId, status = :jobStatus WHERE file_name = :fileName
`
return msg-
Add a mysql node after the function node.
-
Configure it to connect to the MariaDB host and database (schema) created earlier in Set up Database.
-
The mysql node executes the SQL statement defined in
msg.topicusing the parameters specified inmsg.payload.
-
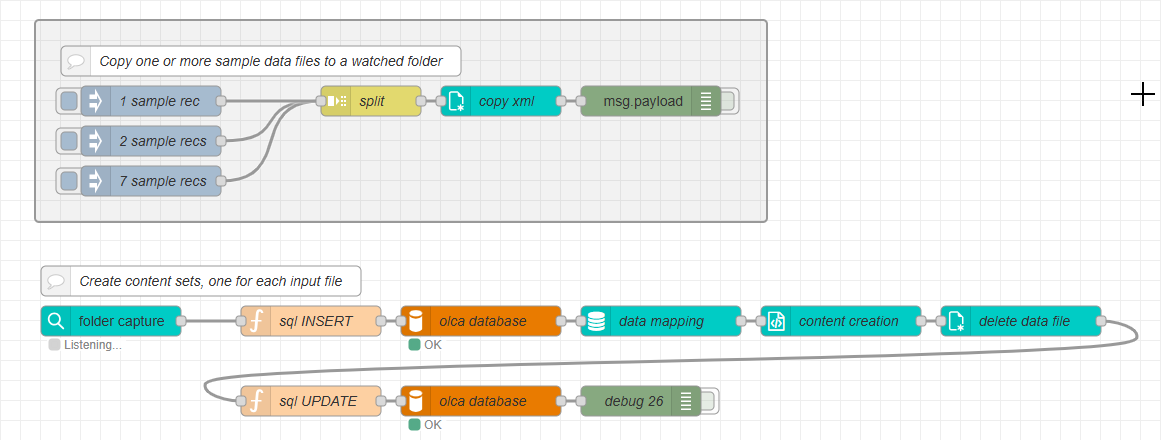
These steps ensure that once a job’s paginated content has been generated, the corresponding database record is updated to reflect its new state. The updated contentSetId allows later flows (e.g., daily or weekly consolidation) to retrieve and process all content generated within a specific period.
Continue to Query Jobs.