A user role is a group of users who are granted identical permissions. Setting up roles is the quickest and most consistent way to apply the same set of permissions to multiple users who have similar responsibilities. You can grant all the permissions at the role level. Then, once the user is made a member of that role, the user inherits all that role’s permissions. Roles are created and managed on the Administration > Users & Roles > Roles page. When you create a new role, you name the role and then select the Upland Qvidian products the users in this role can use, and their system permissions. Once you set up your roles, you can now create your individual User IDs and assign the appropriate role(s) to each User ID.
Example: For an example of roles and permissions, see the "Example of Permissions by Role" section of Permissions.
Search roles
- To search for a role, enter text into the search box at the top right of the grid, and click the Search
 icon or Enter.
icon or Enter. - To re-display all records in the grid, delete the entire entry in the box by clicking the X.
Filter the grid
Use the advanced filters to display specific records quickly on the grid.
- Hover over the column header until you see the Filter
 icon appear.
icon appear. -
Click the Filter
 icon to display the following dialog to set filtering parameters:
icon to display the following dialog to set filtering parameters:- Text Columns: Select either Contains All, Contains Any, Matches Any, Matches Exactly, Starts with, Ends with, Is Empty, Is Not Empty, or Does Not Contain from the Operator dropdown menu. The Contains All, Contains Any, Does Not Contain, and Matches Any operators allows you to enter more than one value by pressing the Enter key after each value. The Starts with and Ends with operators allow you to enter a text value to find. The Is Empty and Is Not Empty operators do not require a value.
- True/False Columns: Select either the Is True or Is False radio button.
- Numeric Columns: Select either Equals, Greater than, Less than, Greater than or equal to, Less than or equal to, Not Equal to, Between, Matches Any, Is Empty, or Not Empty from the Operator dropdown menu. The Between operator shows two fields for the starting and ending values of the range you want to find. Is Empty and Not Empty operators do not require a value. All other operators require a single value.
- Date Columns: Select either On, After, Before, Between, Is Empty, or Not Empty from the Operator dropdown menu. The Between operator shows two fields for the starting and ending dates of the range you want to find. Is Empty and Not Empty operators do not require a value. All other operators require a single value.
- Click Apply.
Tip: To clear the filter, click the Clear Filter ![]() icon in the header, and then click Clear. You can also click out of the filter dialog to close it.
icon in the header, and then click Clear. You can also click out of the filter dialog to close it.
Sort columns
- To sort columns chronologically or alphabetically, click the column header name. The records will display in ascending order.
- To switch from ascending to descending order, click the selected column header name again.
Select grid rows
- Select your desired grid row(s) using the checkboxes or by clicking the rows and using CTRL+CLICK or SHIFT+CLICK to select multiple records.
Default v Compact column mode
You can switch between the default and compact column modes. Unless updated, the grid will remain in default mode. Compact mode shortens the height of the grid rows.
- To switch between the modes, go to My Preferences within the header Profile menu and select the Default and/or Compact radio buttons.
Using the Everyone Role
The Everyone role is designed for situations in which you want to grant every user the same permissions. For example, if your company grants all its users the Change Password and Change Basic Personal Info (Address, Phone, etc.) permissions, you can use the Everyone role to quickly grant those permissions to all users rather than doing so individually. Then, all other permissions granted users are performed via standard role by role, or user by user basis. The Everyone role is a fixed role that cannot be removed. Please note the following considerations when using this role:
- You can assign permissions and product licenses to this role just like any other role.
- Any permission selected for this role will be granted to all users and cannot be removed for any user. If you do not want specific users to have a permission selected for this role, you would need to clear the permission and then grant the permission on a user by user basis.
- Because all users are members of this role, there is no option to add or remove users.
ProSearch
ProSearch is a limited Upland Qvidian license with limited access to specific features for users who primarily work with content in the library and answer assigned questions in created documents. Administrators can assign a ProSearch license to users or roles by selecting ProSearch as the product in user properties under Role Memberships or in the role properties under Role Information.
Examples of ProSearch users include:
- Subject Matter Experts (SMEs) could use it to easily respond to questions assigned to them from an RFP created document and/or submit new content suggestions.
- Sales Reps may use it for general consumption of content needed in interactions with prospects.
- Users who need access to library but no automation.
ProSearch users can do the following:
- Search the library and work with content records within the library, including:
- Uploading and Bulk loading content.
- Editing content and content record properties.
- Assigned Questions: Answer assigned questions in an RFP created document.
- Provide general or content feedback. Content feedback is created for content records or bundles. General feedback is not associated with a specific content record or document type.
- Bookmark frequently used content so that they can quickly access it without browsing or searching the library.
- Manage their user information, set and reset preferences, and bookmark the Qvidian URL.
- Download the Qvidian Add-Ins for Microsoft Office. Add-ins are only required for users who architect document types and want the option to include Structured Content, Agenda Slide, and Dynamic Slide components in document types, and users working with RFP questions in created documents.
Note: Access to the features above are dependent on application permissions.
ProSearch users cannot:
- Work in the new projects interface.
- Assign or work on content review jobs.
- Create links.
- Create and build documents.
- Send email notifications.
- Access Reports or Administration
Permissions by Role Report
It is a common practice to design a plan for user, role and permissions prior to administrating them in Upland Qvidian. You can do this by running the Permissions - By Role report that prints all the permissions with the roles across the top and indicates which permission is applied to each role. If you have not created roles yet, the roles columns will be blank spaces that you can fill in with the roles you intend to create. You can also run the report with each new release to help you manage permissions.
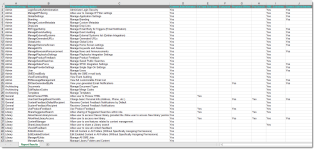
Example of Permissions - By Role report. Click to enlarge.
To run the Permission - By Role report, follow the tasks below.
- Select Reports from the navigation menu.
- Navigate to the Permissions - By Role report using one the methods below:
- Click the navigation arrows at the bottom of the report list grid.
- Type "Permissions" in the Search within grid box and press Enter.
- Highlight Permissions - By Role in the report list grid.
- Click View in Excel. You are prompted to open or save the report.
Note: The License usage panel in the Roles page (Administration > Users & Roles > Roles), lists the Upland Qvidian application licenses that are available for use to help you make decisions when adding or removing users.
When working with roles permissions, keep in mind the following:
- Adding or deleting a role permission changes it for all users assigned to the role.
- You can add a permission for a role that has not been previously granted as a role permission, but you cannot remove a user permission for a user that was previously assigned to the user as a role permission.
- A user can be assigned to more than one role and, therefore, role permissions may overlap. For example, a user is assigned to role 1 and role 2. Role 1 has permission A and permission B and role 2 has permission A and permission C , therefore, the user has A, B, and C permissions. If you removed permission C from role 2, then the user would have permission A and permission B. But if you removed permission A from role 1, the user would still have permission A, because it is given to the user by role 2.